
















cat no | io1035
ioMicroglia TREM2 R47H/R47H
Human iPSC-derived Alzheimer's disease model
-
Cryopreserved human iPSC-derived cells powered by opti-ox, that are ready for functional experiments after 4 days
-
Engineered to investigate the effect of the mutant TREM2 protein in Alzheimer's disease
-
Consistently perform key phagocytic and cytokine secretion functions, and are co-culture compatible

Human iPSC-derived microglia Alzheimer's disease model

ioMicroglia TREM2 R47H/R47H show a similar response of phagocytosis of E.coli particles compared to the genetically matched wild-type control
Phagocytosis was analysed at day 10 post-revival after incubation with 1 µg/0.33 cm2 pHrodo RED labelled E. coli particles for 24 hours with images acquired every 30 mins on the Incucyte. The graphs display the proportion of cells phagocytosing E. coli particles (left) and the fluorescent intensity per cell (right), and shows that ioMicroglia TREM2 HET have a reduced phagocytic capacity, whereas the ioMicroglia TREM2 Hom display a similar phagocytosis response compared to the genetically matched WT control ioMicroglia Male. Three technical replicates were performed. Seeding density 60,000 cells/cm2.
View the phagocytosis protocol used to generate this data.

Disease model cells demonstrate phagocytosis of Amyloid β-42 particles in a similar manner to the genetically matched wild-type control
Phagocytosis was analysed at day 10 post-revival after incubation with 500 nM AF488 labelled Amyloid β-42 (AnaSpec) for 24 hours with images acquired every 30 mins on the Incucyte. The graphs display the proportion of cells phagocytosing (left), and the fluorescence intensity per cell displaying degree of phagocytosis (right), and shows that ioMicroglia TREM2 Het and the ioMicroglia TREM2 Hom cells display a similar phagocytosis response compared to the WT control ioMicroglia Male. Three technical replicates were performed. Seeding density 60,000 cells/cm2.

Disease model cells show a pro-inflammatory cytokines response to Amyloid β-42 stimulation
ioMicroglia TREM2 Het, ioMicroglia TREM2 Hom, and the genetically matched WT control ioMicroglia Male were stimulated for 24 hours with LPS (100 ng/ml) and IFNɣ (20 ng/ml), or synthetic Amyloid β-42 oligomers (10 μM, StressMarq). Supernatants were harvested after 24 hours and analysed with using the MSD V-PLEX Proinflammatory Kit. Secretion levels were normalised to cell count per field of view (FOV) to account for variations in cell density. Seeding density 80,000 cells/cm2.
A clear response to LPS+IFNɣ and Amyloidβ-42 is seen in both disease model cell types.
View the cytokine release protocol used to generate this data.

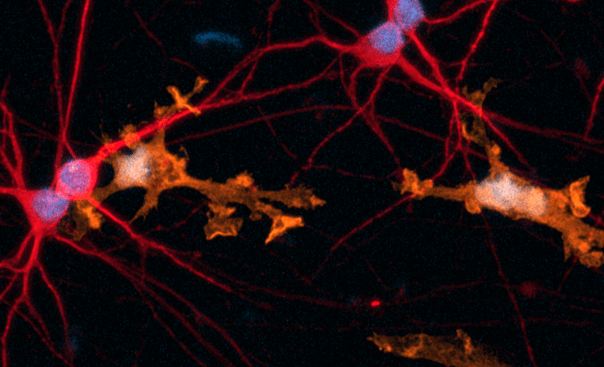
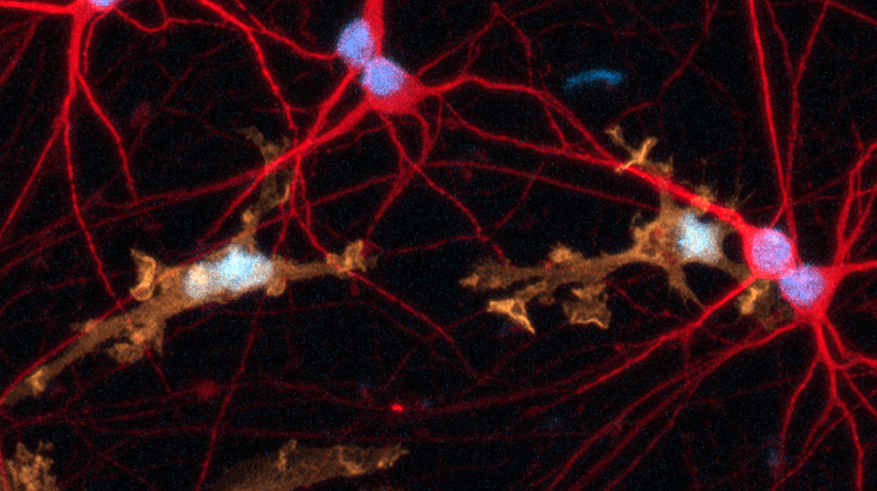
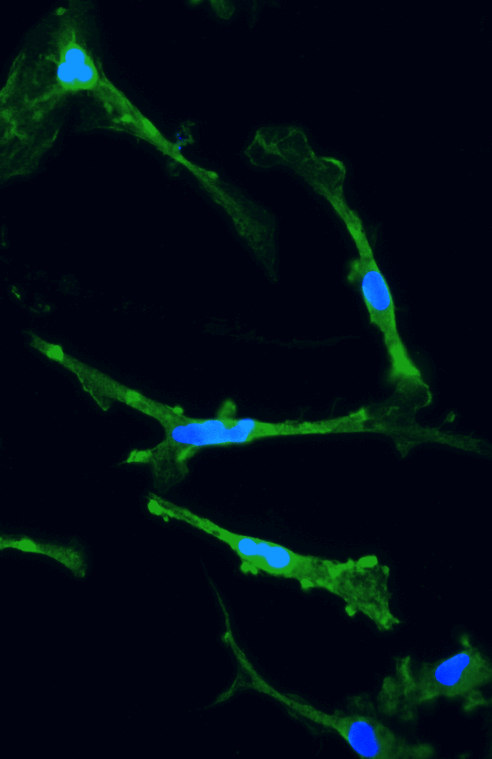
Disease model cells express key microglia markers comparably to the genetically matched wild-type control
Immunofluorescent staining on day 10 post-revival demonstrates similar homogenous expression of microglia marker IBA1 and ramified morphology in ioMicroglia TREM2 R47H/R47H disease model cells compared to the genetically matched wild-type (WT) control. 100X magnification.

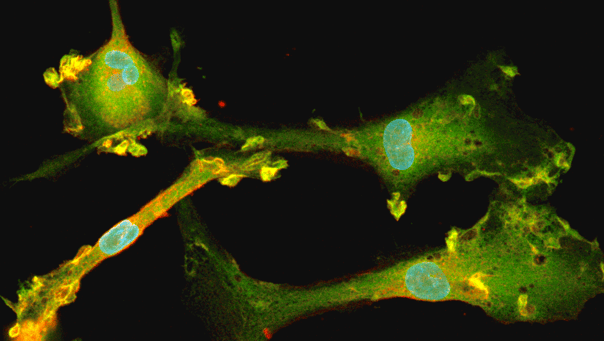
Disease model cells express key microglia markers comparably to the genetically matched wild-type control
Immunofluorescent staining on day 10 post-revival demonstrates similar homogenous expression of microglia marker P2RY12 and ramified morphology in ioMicroglia TREM2 R47H/R47H disease model cells compared to the genetically matched wild-type (WT) control. 100X magnification.

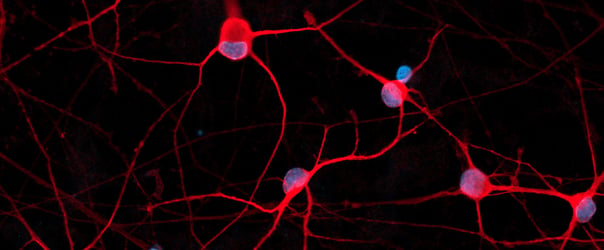
Disease model cells show expected ramified morphology by day 10
ioMicroglia TREM2 R47H/R47H disease model cells mature rapidly and key ramified morphology can be identified by day 4 and continues through to day 10, similarly to the WT control. Day 1 to 10 post-thawing; 100x magnification.
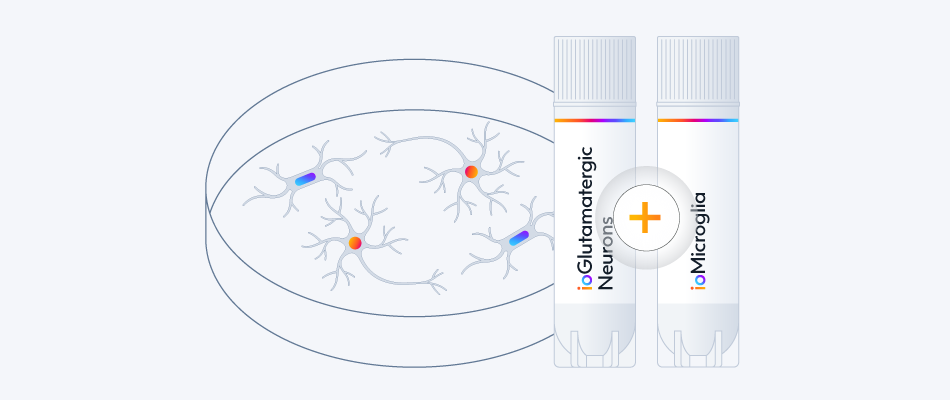
Female donor-derived ioMicroglia form co-cultures with ioGlutamatergic Neurons
ioGlutamatergic Neurons (io1001) were cultured to day 10 post-thaw. Female donor-derived ioMicroglia (io1029) cultured to either day 1 or day 10 post-thaw were added directly to day 10 ioGlutamatergic Neurons. The co-cultures were maintained for a further 6 days. Representative video showing that female donor-derived ioMicroglia form a stable co-culture with ioGlutamatergic Neurons. Live imaging was performed in 6.5-minute intervals over a time period of 3 hours and 31 minutes using the 3D Cell Explorer 96focus Nanolive Imaging system.

ioMicroglia are efficiently transfected with mRNA encoding GFP
ioMicroglia Male are efficiently transfected and show sustained long-term expression of mRNA encoding GFP. Cells were imaged throughout the experiment to assess transfection efficiency and evaluate potential cytotoxic effects of the transfection protocol. Day 4 images were captured prior to transfections on the same day.
Download the step-by-step protocol for lipid-based delivery of synthetic mRNA into ioMicroglia.
Vial limit exceeded
A maximum number of 20 vials applies. If you would like to order more than 20 vials, please contact us at orders@bit.bio.




Hoescht(blue)TUBB3(blue)_day4.png?width=604&name=bit.bio_ioGlutamatergic%20Neurons_60xMAP2(red)Hoescht(blue)TUBB3(blue)_day4.png)






_MAP2(R)_Tubb3(B)_Hoechst(B)_20x_merge-comp.jpg?width=604&name=Colour%20webinar%20with%20it-bio%20ioGlutamatergic%20Neurons_VGLUT2(G)_MAP2(R)_Tubb3(B)_Hoechst(B)_20x_merge-comp.jpg)