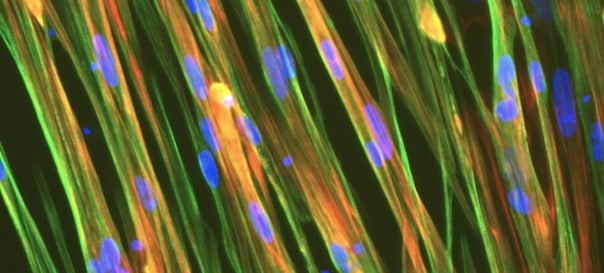
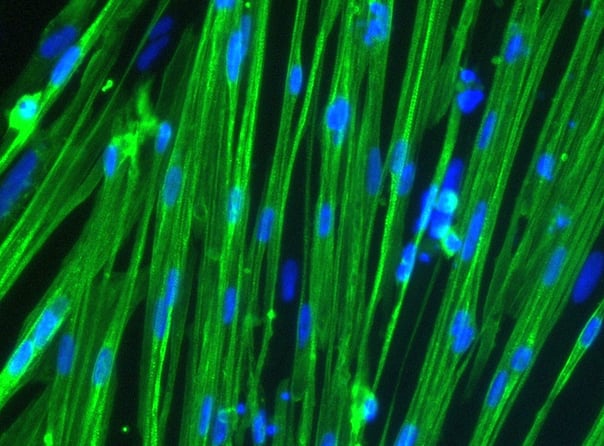
Human iPSC-derived muscle cells
Consistent, defined and scalable human iPSC-derived skeletal myocytes for musculoskeletal disorders (MSD) research
Significant advances are being made in the study of musculoskeletal disease. Where conditions like Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) were once seen as untreatable, hope now swells as gene therapies advance into the market. Critical to the study and treatment of conditions like DMD is the use of physiologically relevant musculoskeletal disease models. As immortalised human muscle cell lines can be difficult to access, and animal myoblast cell lines are phenotypically distinct from their in vivo counterparts, many in the field are now turning to a more physiologically accurate source of cells: iPSC-derived myocytes [1].
bit.bio’s deterministic cell programming technology (known as opti-ox™) makes it possible to generate functional human skeletal muscle cells with unmatched lot-to-lot consistency from iPSCs on a nearly limitless scale (all without the challenges typically associated with myocyte differentiation). Both wild-type and disease-specific myocytes are readily available, enabling researchers to study skeletal myocytes in vitro with ever more translational power.
Leveraging genetically matched controls, human iPSC-derived skeletal myocytes containing DMD mutations can be used to screen prospective therapeutics, including exon-skipping therapies and other advanced drug modalities.
Strengthen your research with bit.bio’s human iPSC-derived skeletal myocytes.
Engineered to meet your workflow with our toolkit of ioWild Type Cells and ioDisease Model Cells
Driving a better understanding of musculoskeletal disease
Dr Rita Horvath, Director of Research in Genetics of Rare Neurological Disorders at the University of Cambridge discusses the mechanical and metabolic roles of myocytes in health and disease, experimental limitations and new opportunities offered by consistent, scalable human myocytes for muscle research and disease modelling.

Browse relevant resources
bit.bio
Dr Mitchell Han
Bi/ond
2023
Bernard, et al
bit.bio
2024
Dr Grace Cooper | Senior Scientist | bit.bio
Human Cell Forum 2025
Session 1 Track 2 | From cells to systems: Building human iPSC-derived models of pain, neuromuscular junctions, and glial dynamics
Dr Sara Martin | Scientist | Axxam
Human Cell Forum 2025
Session 3 | Making complex human biology compatible with modern drug discovery workflows
DOC-2849 3.0
bit.bio
2025
Dr Will Bernard | Director of Cell Type Development | bit.bio
Prof Hagan Bayley | University of Oxford
Dr Mark Kotter | Founder and CEO | bit.bio
Dr Luke Flatt | Senior Scientist | Charles River Laboratories
Dr Will Bernard | Senior Scientist | bit.bio
Dr Marieke Aarts | Principal Scientist | Bi/ond
Amanda Turner | Senior Product Manager | bit.bio
References
1. Danisovic L, Culenova M, Csobonyeiova M (2018) Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Modeling and Therapy. Cells. 2018 Dec 7;7(12):253. doi: 10.3390/cells7120253. PMCID: PMC6315586 PMID: 30544588




/ioSkeletal-Myocytes-DMD-Exon-52-Deletion-hero.webp?width=1276&height=1190&name=ioSkeletal-Myocytes-DMD-Exon-52-Deletion-hero.webp)
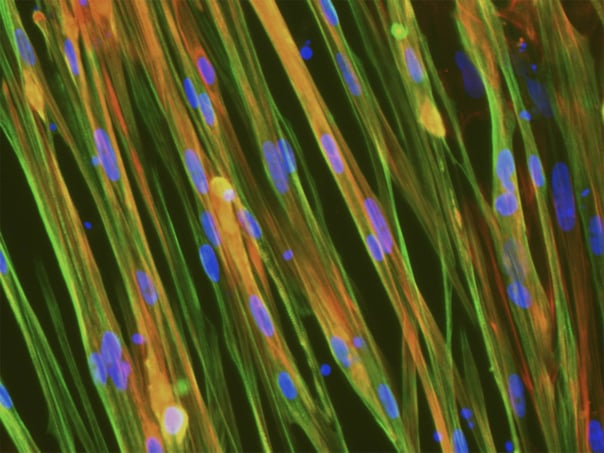
-1%20(1).png?width=604&name=horizontal_ioSkeletal-Myocytes-Muscle-Bundle-Biond-ICC-SAA-Actin%20(1)-1%20(1).png)
.png?width=604&name=ISSCR24-DMD-Exon44-3D-muscle-bundle%20(1).png)





.jpeg?width=604&name=New%20Project%20(13).jpeg)