Poster
Validation of ALS-relevant phenotypes in precision reprogrammed iPSC-derived glutamatergic Neurons containing a TDP-43 M337V mutation.
This poster, originally presented by Charles River at Neuroscience 2022 (SfN), presents experimental data showing that ioGlutamatergic Neurons containing a TDP-43 M337V mutation are a relevant, translational in vitro drug discovery model for ALS.
View poster
This poster, originally presented by Charles River at Neuroscience 2022 (SfN), presents experimental data showing that ioGlutamatergic Neurons containing a TDP-43 M337V mutation are a relevant, translational in vitro drug discovery model for ALS.
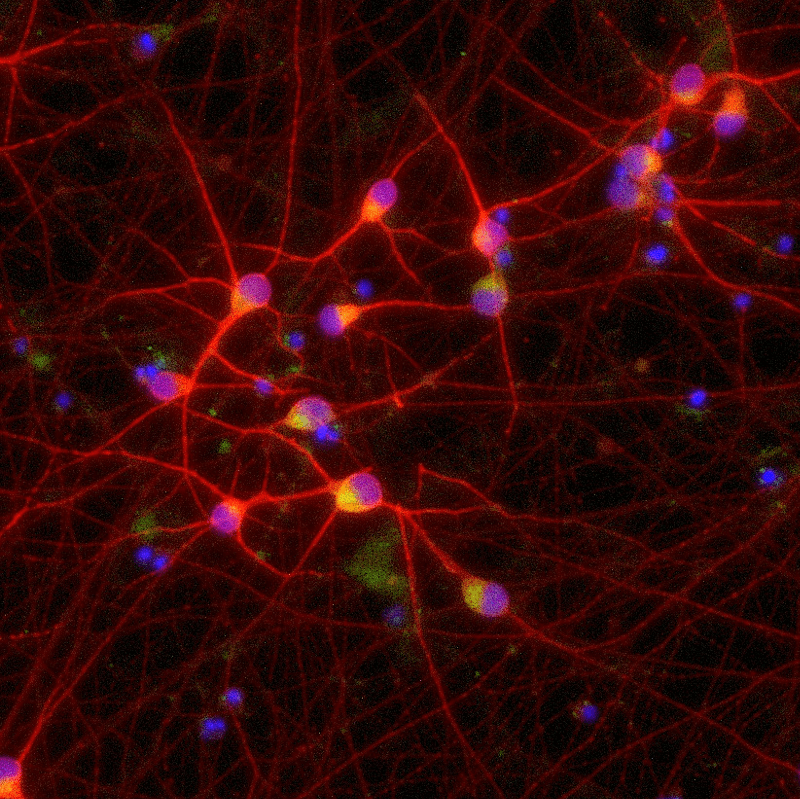
In this poster, Charles River Laboratories assessed whether ioGlutamatergic Neurons TDP-43 M337V from bit.bio was a relevant translational model for vitro drug discovery for ALS. The disease model consists of induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived glutamatergic neurons developed by bit.bio, generated using opti-ox precision cellular reprogramming, and CRISPR-edited to contain the TDP-43 M337V mutation seen in rare genetic forms of ALS. This poster shows data from experiments analysing TDP-43 mislocalisation and phosphorylation, and STMN-2 mis-splicing in the presence and absence of MG-132, a proteasomal inhibitor.
In this poster, you will explore:
- How ioGlutamatergic Neurons TDP-43 M337V were assessed for their relevance as an in vitro ALS disease model.
- How robust assays were established for assessing TDP-43 mislocalisation and phosphorylation, and STMN-2 mis-splicing in this disease model.
- How ioGlutamatergic Neurons TDP-43 M337V show significantly increased TDP-43 mislocalisation and phosphorylation.
- How ioGlutamatergic Neurons TDP-43 M337V show significantly increased STMN-2 mis-splicing
- How these results were confirmed in the presence of an isogenic control, also developed by bit.bio